DHU
Domain-Hallucinated Updating for Multi-Domain Face Anti-spoofing (AAAI-2024)
Domain-Hallucinated Updating for Multi-Domain Face Anti-spoofing
Chengyang Hu1*, Ke-Yue Zhang2*, Taiping Yao2, Shice Liu2, Shouhong Ding2, Xin Tan3, Lizhuang Ma1,3,4
1 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
2 Youtu Lab, Tencent
3 East China Normal University
4 MoE Key Lab of Artificial Intelligence, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
(AAAI 2024)
Paper · Code · Project Page · 中文解读
Abstract
Multi-Domain Face Anti-Spoofing (MD-FAS) is a practical setting that aims to update models on new domains using only novel data while ensuring that the knowledge acquired from previous domains is not forgotten. Prior methods utilize the responses from models to represent the previous domain knowledge or map the different domains into separated feature spaces to prevent forgetting. However, due to domain gaps, the responses of new data are not as accurate as those of previous data. Also, without the supervision of previous data, separated feature spaces might be destroyed by new domains while updating, leading to catastrophic forgetting. Inspired by the challenges posed by the lack of previous data, we solve this issue from a new standpoint that generates hallucinated previous data for updating FAS model. To this end, we propose a novel Domain-Hallucinated Updating (DHU) framework to facilitate the hallucination of data. Specifically, Domain Information Explorer learns representative domain information of the previous domains. Then, Domain Information Hallucination module transfers the new domain data to pseudo-previous domain ones. Moreover, Hallucinated Features Joint Learning module is proposed to asymmetrically align the new and pseudo-previous data for real samples via dual levels to learn more generalized features, promoting the results on all domains. Our experimental results and visualizations demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art competitors in terms of effectiveness.
Method
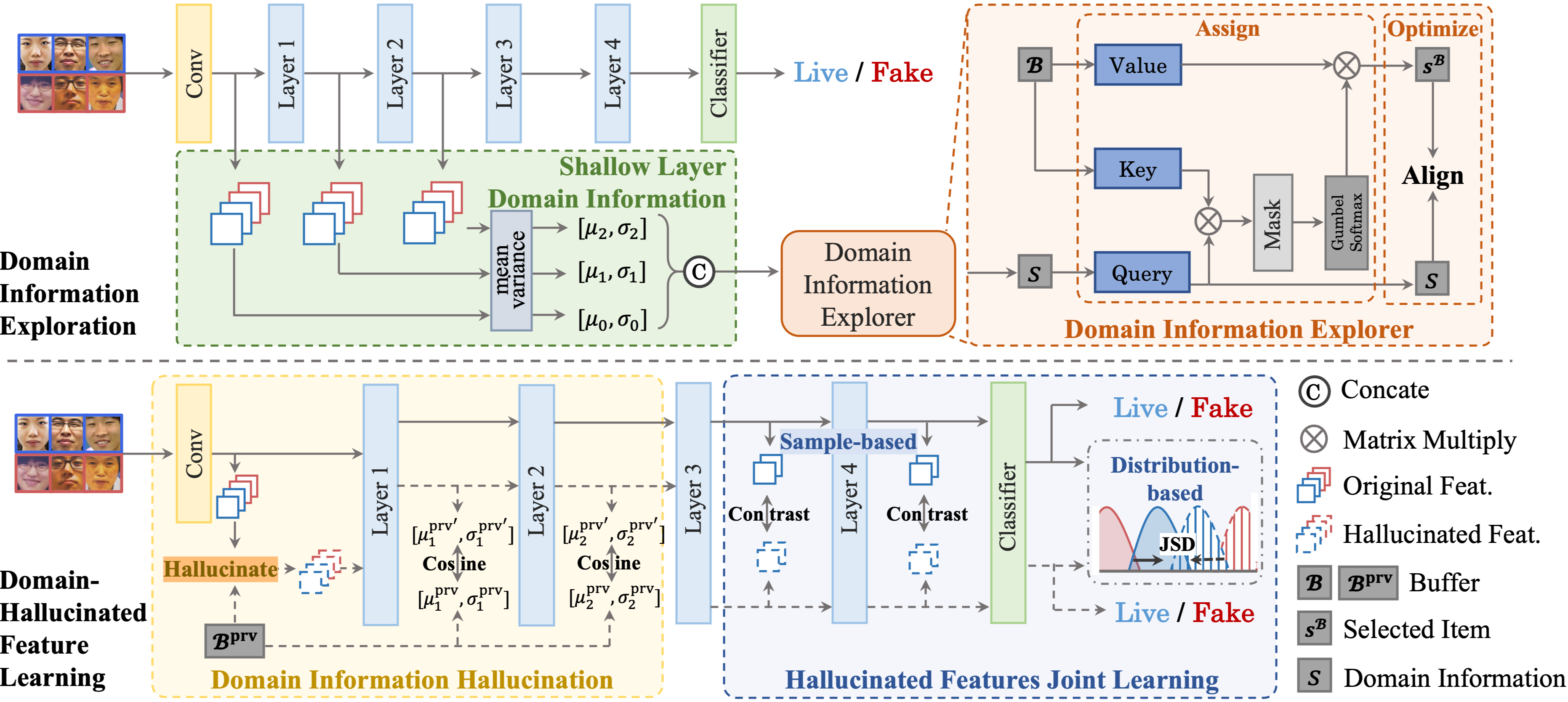
The overall structure of proposed Domain-Hallucinated Updating (DHU) framework. First, we propose Domain Information Explorer to learn effective domain information in shallow layers. Also, we first propose Domain Information Hallucination module to hallucinate the previous domain feature to prevent the forgetting issue. After obtaining the pseudo-previous and new domain feature, we design Hallucinated Features Joint Learning to align the real input features from sample-based view and distribution-based view for generalizability.
Result
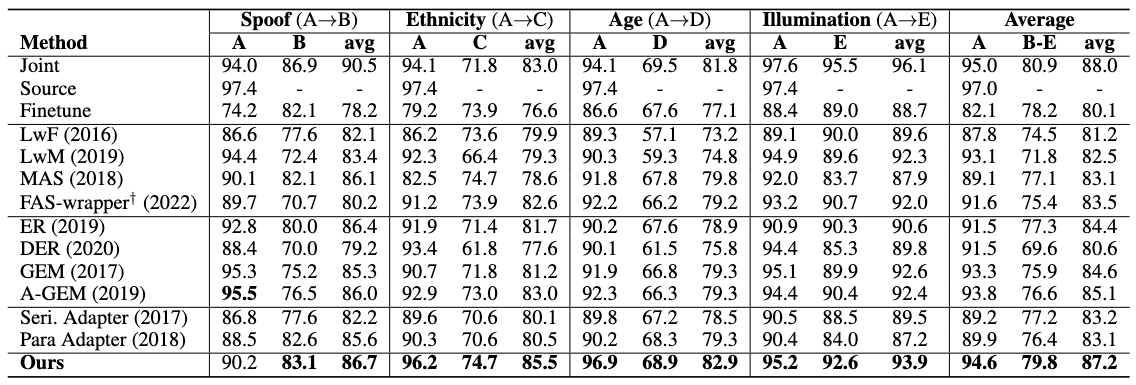
The performance reported in TPR@FPR=0.5%. The model first trains on the source dataset (A) and then train on other datasets (B-E). avg indicates the average performance on two datasets. Bolded scores indicate the best performance. (\dag): We re-implement FAS-wrapper with ResNet-18 by inserting stacked CNN models as Discriminator into every ResNet layer.
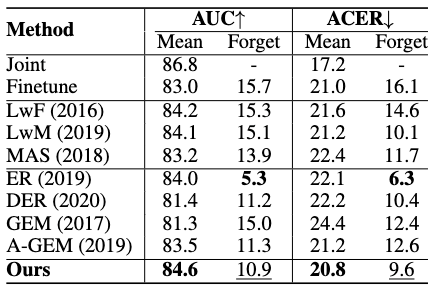
The performance reported in AUC and ACER on long sequence CASIA -> OULU -> Idiap -> MSU. Bolded scores show the best performance. Underlined scores show the second best performance.
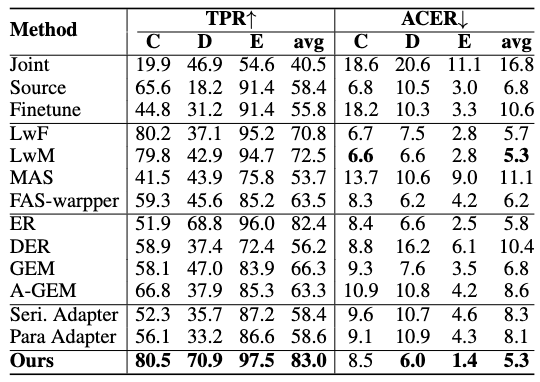
The performance on unseen domains in TPR@FPR=0.5% and ACER. The model first trains sequentially with datasets A and B and tests on C-E. The result in Serial, and Parallel Res-Adapter is the average result with different adapters.
Visualization
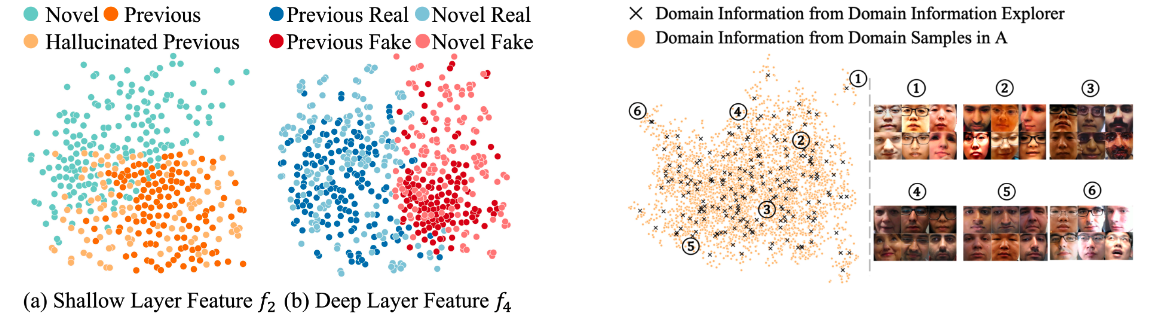
- Left: The t-SNE visualization of the feature from different layers. (a) shows the previous, hallucinated previous, and new feature in the shallow layer ((f_2)) (b) shows the previous and new feature in the deep layer ((f_4)).
- Right: The t-SNE visualization of the previous domain information distribution. The right pictures show examples from different domain information groups.
Conclusion
In this paper, we propose a novel Domain-Hallucinated Updating (DHU) framework to address the challenging task of Multi-domain Face Anti-Spoofing (MD-FAS). First, we introduce Domain Information Explorer in the previous training stage that learns representative domain information buffer (\mathcal{B}). Then, Domain Information Hallucination module is designed in the new training stage to generate pseudo-previous domain information to prevent forgetting. Additionally, we devise Hallucinated Features Joint Learning module to utilize pseudo-previous and new domain features, which aligns real samples’ features from sample-based and distribution-based views to improve model’s generalizability. The experimental results and visualizations demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms other competitors.
Citing Our Work
If you find our work is useful in your reasearch, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{hu2024domain,
title={Domain-Hallucinated Updating for Multi-Domain Face Anti-spoofing},
author={Hu, Chengyang and Zhang, Ke-Yue and Yao, Taiping and Liu, Shice and Ding, Shouhong and Tan, Xin and Ma, Lizhuang},
booktitle={Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
volume={38},
number={3},
pages={2193--2201},
year={2024}
}
Acknowledgments
Our work is based on the following opensource project. We thank their authors for making the source code publically available.