HPDR
Rethinking Generalizable Face Anti-spoofing via Hierarchical Prototype-guided Distribution Refinement in Hyperbolic Space (CVPR-2024 Highlight)
Rethinking Generalizable Face Anti-spoofing via Hierarchical Prototype-guided Distribution Refinement in Hyperbolic Space
Chengyang Hu1*, Ke-Yue Zhang2*, Taiping Yao2, Shouhong Ding2, Lizhuang Ma1,3
1 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
2 Youtu Lab, Tencent
3 MoE Key Lab of Artificial Intelligence, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
(CVPR 2024 Highlight)
Paper · Code · Project Page · 中文解读
Abstract
Generalizable face anti-spoofing (FAS) approaches have drawn growing attention due to their robustness for diverse presentation attacks in unseen scenarios. Most previous methods always utilize domain generalization (DG) frameworks via directly aligning diverse source samples into a common feature space. However, these methods neglect the hierarchical relations in FAS samples which may hinder the generalization ability by direct alignment. To address these issues, we propose a novel Hierarchical Prototype-guided Distribution Refinement (HPDR) framework to learn embedding in hyperbolic space, which facilitates the hierarchical relation construction. We also collaborate with prototype learning for hierarchical distribution refinement in hyperbolic space. In detail, we propose the Hierarchical Prototype Learning to simultaneously guide domain alignment and improve the discriminative ability via constraining the multi-level relations between prototypes and instances in hyperbolic space. Moreover, we design a Prototype-oriented Classifier, which further considers relations between the sample and prototypes to improve the robustness of the final decision. Extensive experiments and visualizations demonstrate the effectiveness of our method against previous competitors.
Method
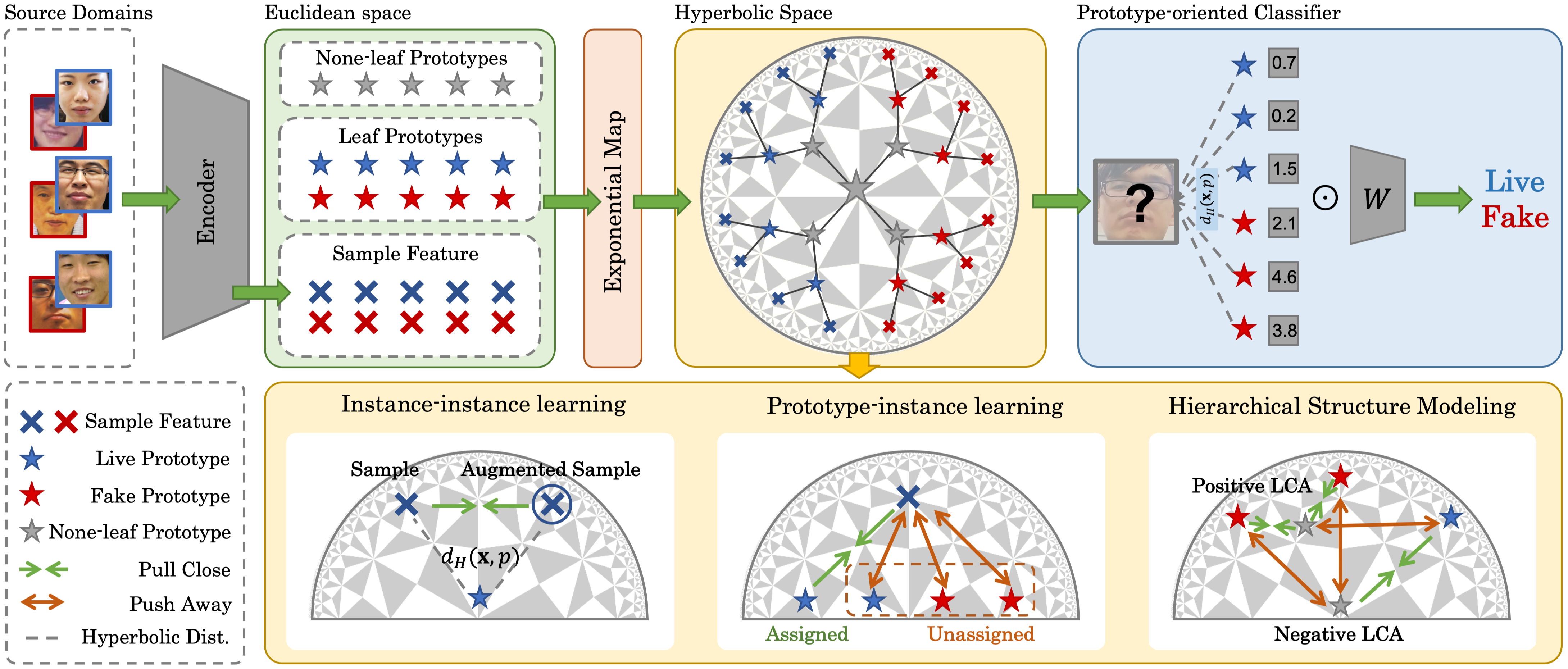
The overall structure of our Hierarchical Prototype-guided Distribution Refinement (HPDR) framework. After we initialize the leaf and none-leaf prototypes. Then Hyperbolic Prototype Learning (HPL) is proposed to simultaneously guide the domain alignment and improve the discriminative ability via multi-level supervision. Moreover, to utilize the relations between the samples and prototypes, we devise Prototype-oriented Classifier for robust decision.
Result
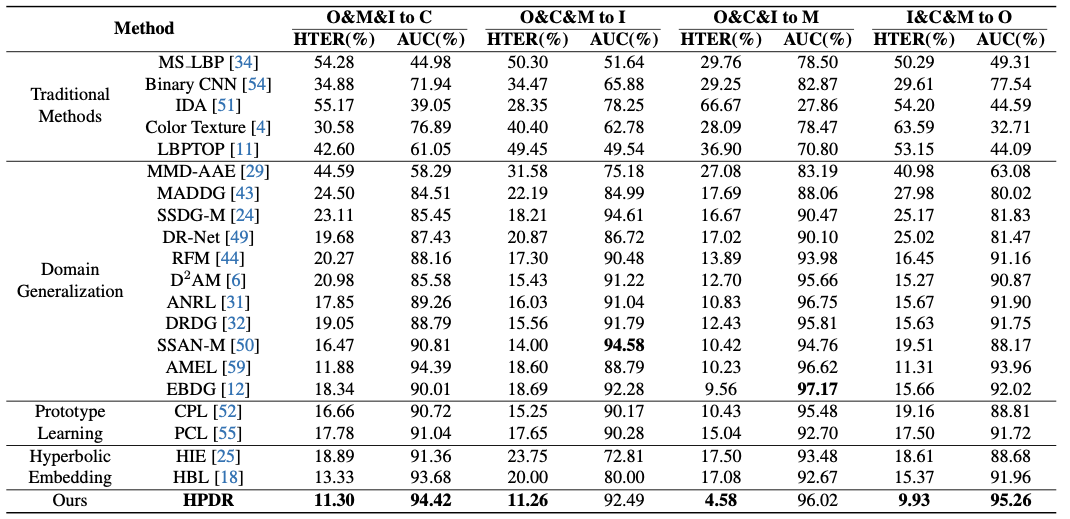
Comparison with face anti-spoofing methods on four testing tasks for domain generalization.
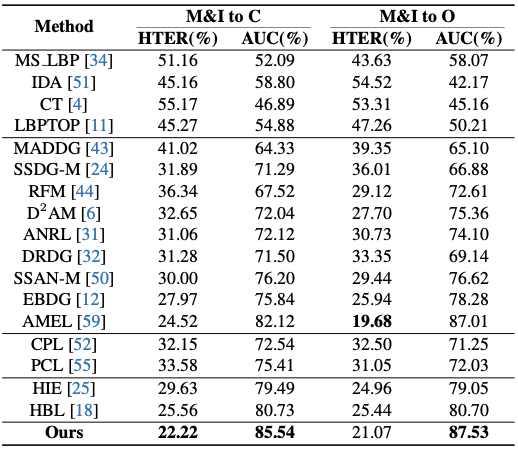
Comparison on limited source domains.
Visualization
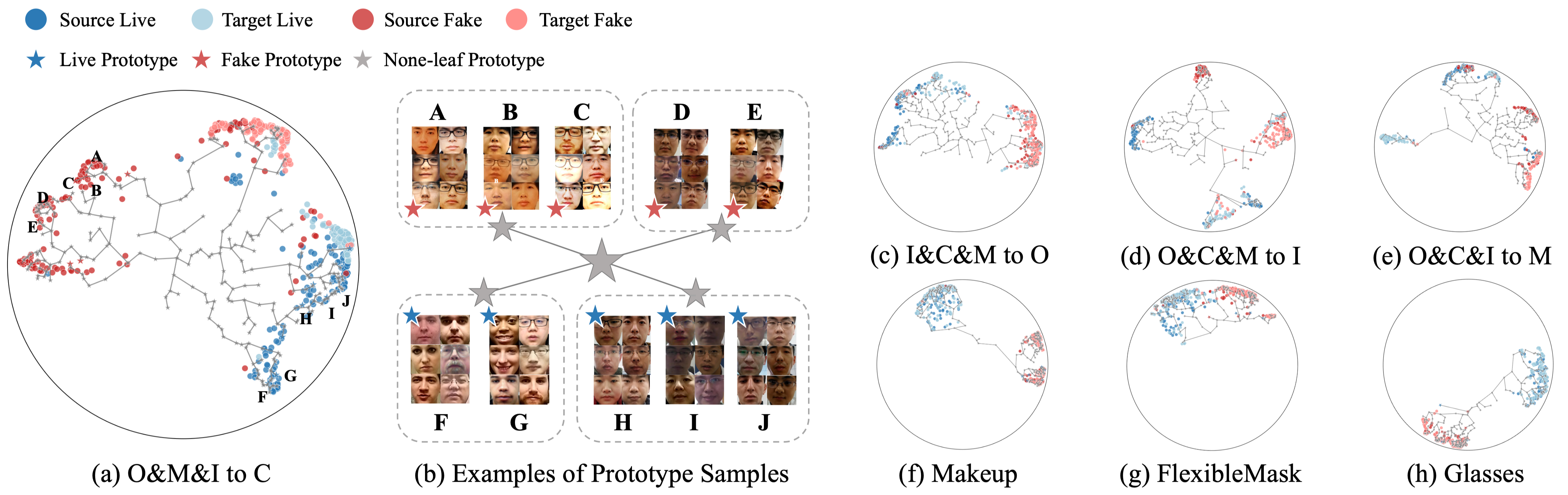
- (a, c-h): The feature visualization on four Leave-One-Out tasks and cross-attack tasks. For every task, we select 300 samples from the source dataset and 300 samples from the target dataset.
- (b): Visualization of the hierarchical structure of the samples in O&M&I to C tasks. We selected 10 prototypes with 6 samples as an example.
Conclusion
In this paper, we propose a novel Hierarchical Prototype-guided Distribution Refinement (HPDR) framework, introducing the prototypes into hyperbolic feature space to obtain a refined domain distribution with a hierarchical structure for generalization. Specifically, we first introduce the leaf and none-leaf prototypes into hyperbolic features space separately for hierarchical structure construction. Then, we propose Hyperbolic Prototype Learning (HPL) to constrain the multi-level relations between features and prototypes. Moreover, we devise Prototype-oriented Classifiers to consider the relations between features and prototypes to improve the robustness of the final decision. Extensive experiments and analysis demonstrate the effectiveness of our method against state-of-the-art competitors.
Citing Our Work
If you find our work is useful in your reasearch, please consider citing:
@InProceedings{hu2024rethinking,
author = {Hu, Chengyang and Zhang, Ke-Yue and Yao, Taiping and Ding, Shouhong and Ma, Lizhuang},
title = {Rethinking Generalizable Face Anti-spoofing via Hierarchical Prototype-guided Distribution Refinement in Hyperbolic Space},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2024},
pages = {1032-1041}
}
Acknowledgments
Our work is based on the following opensource project. We thank their authors for making the source code publically available.